It’s Frustrating-The Verdict Is Still Out
In this blog I will update what we know about Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19
Amazing how a small viral particle, so small it must be viewed under a microscope to be seen, can create a pandemic that has turned the world upside down. The new corona virus or SARS-CoV-2 has proven itself to be a lethal and stealth organism, one that is mightier than the most powerful countries in the world.
And yet, the Virus is really a wimp easily destroyed by soap and water.
Updated studies shows that the new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, survives for no more than a day on cardboard, and about two to three days on steel and plastic. They cannot travel or spread on their own. They are dependent on their hosts for survival. Without human interaction the Virus cannot live. A six-foot buffer between an infected individual and a non infected individual is all that is needed to stop the spread.
We can’t stay quarantined forever. Eventually we will need to return to life as before the pandemic.
The race is own for a vaccine to prevent the Virus from spreading next year. For now, the pressing issue is to find a drug or drugs to treat those already infected.
Unfortunately, antivirals don’t provide the “miracle” affects the way antibiotics can against bacteria. The well-known antiviral medication, Tamiflu, can shorten the duration of the flu by a day or two, but does not outright cure it.
And while the antivirals for HIV and hepatitis C have been successful, they must be taken as cocktails of two or three different drugs at a time. Fortunately, at least for now, unlike other viruses, the SARS-CoV-2, does not seem to mutate or change its form.

As the infection progresses, the lungs clog with dead cells and fluid, making breathing more difficult. The immune system fights back, releasing white blood cells to attack the virus, causing inflammation and fever. If the immune system over reacts it can trigger are cytokine storms, potentially deadly reactions.
Researchers are frantically looking for drugs to reduce the ability of the Virus to attach to or enter the cell to prevent cytokine storms.
The World Health Organization is launching a multinational set of trials testing the efficacy of interferon, chloroquine, lopinavir, and ritonavir. This should provide us with some information, but right now a lot of things are being thrown at COVID-19 with no clear evidence they are effective.
One of the most talk about drugs, Hydroxychloroquine, has shown promise.
I continue to get questions about this drug. There is quite a bit of hype surrounding it and not a lot of concrete data.
These drugs work for autoimmune disease largely because they suppress the immune system, which in autoimmune disease has become over reactive.
In some animal studies, the drugs have actually prevented the immune system from responding to an infection.
One theory-SARS-CoV-2 requires an acidic environment. Hydroxychloroquine is an alkaline compound, so it raises the pH levels of the host environment, preventing the virus from releasing its genes for copying.
Doctors are reluctant to recommend these drugs without more research. They point out that the side effects including heart attack and heart failure are one of the reasons those with COVID-19 die. Could these drugs be making things worse?
Serious side effects that include-blindness due to retinal injury, loss of consciousness due to low blood sugar, suicidal behavior, heart failure, potentially lethal interactions with other drugs, lethal heart rhythm disturbances and yes, death.
These drugs have been shown in vitro (in a test tube, not a living organism) to have a broad spectrum of antiviral activities. Although they have never been shown to have clear antiviral activity in humans against any virus, they have become widely used in China to treat COVID-19.
Despite the widespread use of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine to treat COVID-19, there are as yet no randomized controlled trials clearly showing it is effective.
Hydroxychloroquine failed to work for the flu and dengue in humans.
The results in HIV have been inconclusive, and the results with hepatitis C have been so slight that it’s never become part of a standard protocol.
A “Systematic Review on the Efficacy and Safety of Chloroquine for the Treatment of COVID-19” suggested similar caution. The authors performed a comprehensive search for everything related to the topic and found very little that had already been published: an in vitro study, two letters, a consensus panel of Chinese experts, a Dutch national guideline, an Italian national guideline and 23 Chinese trials.
A letter by Chinese authors reported at a news briefing from the State Council of China had indicated that “Chloroquine phosphate… had demonstrated marked efficacy and acceptable safety in treating COVID-19 associated pneumonia in multicentre clinical trials conducted in China.” The authors also stated that these findings came from “more than 100 patients” included in the trials.
A non-randomized French trial of hydroxychloroquine suggested the drug virologically cured 15 out of 26 people, while it nauseated one, put three in ICU, and killed one. Because it wasn’t randomized, it isn’t clear whether the cure or the worsening represent true effects of the drug, but if we are to regard the cure as a real effect, we also have to regard the worsening as a real effect, suggesting that if it works it might have a high risk profile. In that study, the drug appeared to help clear the virus from the bodies of 26 patients who were given the medication, based on samples taken from nasal swabs. Experts have criticized the design of the study, calling it interesting but far from definitive.
Another Chinese randomized controlled trial found no difference at all between the use of hydroxychloroquine and standard treatment. The standard treatment was bed rest, oxygen inhalation, symptomatic support, neubulized interferon, lopinavir and ritonavir (two antivirals), and, when necessary, antibacterials. The two antivirals in the standard treatment have also been shown to have no effect against another “standard treatment” in another randomized trial.
The report published by the Journal of Zhejiang University in China showed that patients who got the medicine didn’t fight off the new coronavirus more often than those who did not get the medicine.
The study itself, like other ones involving hydroxychloroquine, was quite small. It involved just 30 patients. Of the 15 patients given the malaria drug, 13 tested negative for the coronavirus after a week of treatment. Of the 15 patients who didn’t get hydroxychloroquine, 14 tested negative for the virus.

Results from those on the front lines have’t always been mixed.
Marcus Zervos, infectious disease doctor for Henry Ford Health System, said they had seen success with hydroxychloroquine therapy in a number of COVID-19 patients. He said those given the drug were able to get off a ventilator and out of the hospital faster.
Dr. Stephen Smith, head of Center for Infectious Diseases and Urban Health in East Orange, New Jersey
He’s treated more than 100 patients and reports success using a combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, an antibiotic.
Smith said only one of about 75 patients receiving a full course of the drugs had to be intubated — have a tracheal tube inserted to use a ventilator. Another 23 patients who were intubated had not received even half of the full course, he said.
“We’ve been using it,” said Dr. Hugh Cassiere, a pulmonologist and medical director of Respiratory Care Services at North Shore University Hospital in Long Island, New York, “But we really haven’t seen any efficacy.”
“I’m not convinced it works,” said Lyn-Kew, adding, “I’ve not seen anybody have anything near what I would call a miraculous recovery because of hydroxychloroquine.”
Dr. Josh Denson, a pulmonary medicine and critical care physician at the Tulane University Medical Center in New Orleans, said that “many patients do fine and tolerate it, but I don’t think it’s making a difference.”
Dr. Ken Lyn-Kew, a pulmonologist in the critical care department at National Jewish Health at hospital in Denver.
He said: “When you give it to somebody who is already super sick, it’s likely not going to make an impact because the damage is already done.” Dr. Ken Lyn-Kew also added: “I’m not convinced it works. I’ve not seen anybody have anything near what I would call a miraculous recovery because of hydroxychloroquine.”
Research Is Underway-
In France, researchers are running a trial with 1,200 health care workers to test prophylactic use of hydroxychloroquine or a combination of two HIV drugs, Lopinavir and Ritonavir. It is expected to take 6 months.
In a 40,000-person trial led by the University of Oxford in England, participants in Asia will receive chloroquine or a placebo, and in Europe, hydroxychloroquine or a placebo. That trial is expected to take a year.
Researchers at Duke University are overseeing a $50 million collaboration across hundreds of American health care systems, which will test 15,000 volunteers. Half the health care workers will take hydroxychloroquine, and half a placebo. It will take some time to know if hydroxychloroquine does or doesn’t help those with COVID-19.
Until we have more scientific studies, we will have to rely on what is or isn’t working on the front lines.
Reports from doctors in my Master Mind groups, including those overseas, are mixed.
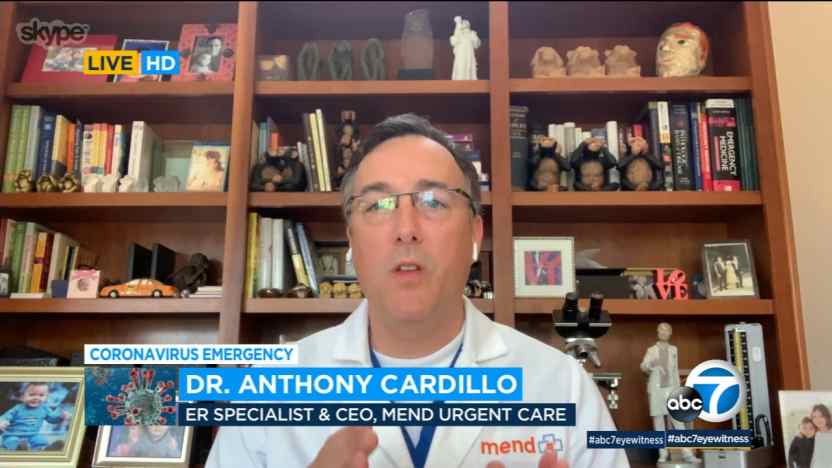
One of the positive reports making the rounds on social media and in the news comes from Dr. Anthony Cardillo, CEO of Mend Urgent Care, with locations in Sherman Oaks Van Nuys and Burbank, California.
On a local news program he shared that he’d seen very promising results when prescribing hydroxychloroquine in combination with zinc for the most severely-ill COVID-19 patients.
–> CLICK HERE for the interview
“Every patient I’ve prescribed it to has been very, very ill and within 8 to 12 hours, they were basically symptom-free,” Cardillo told Eyewitness News.
He said he has found it only works if combined with zinc. The drug, he said, opens a channel for the zinc to enter the cell and block virus replication.
Could zinc be the missing link in some of these failed trials?
Studies have shown that zinc has an ability to block the replication of the corona virus group. We don’t know if the combination of hydroxychloroquine and zinc is more affective than hydroxychloroquine alone.
Its theorized that hydroxychloroquine is a zinc ionophore- a compound that helps transport zinc from outside the cell to the inside of the cell. This may or may not be why hydroxychloroquine is more effective when combined with zinc as some doctors are reporting. We do know that zinc plays a prominent role in beefing up the immune response.
More On Zinc
A study published in 1996 shuffled 100 Cleveland Clinic employees who self-reported catching colds into two groups. Fifty took lozenges containing 13.3 milligrams of zinc gluconate – the dosage of today’s Cold-Eeze and other over-the-counter lozenges – every two hours as long as they had cold symptoms.
Fifty others took placebo lozenges. The study was double-blind, so neither patients nor researchers knew which patients had the placebo. The findings: the zinc group cleared symptoms more than three days earlier – 4.4 days versus 7.6 days of the placebo group, and, until that point, suffered fewer days with cough, headache, hoarseness, nasal congestion, and sore throat (fever, muscle aches, scratchy throat and sneezing remained similar during the cold’s duration).
A Cochrane review of zinc for the common group of cold viruses, updated in 2013 summarized 18 randomized controlled trials involving 1,781 participants across all age groups found that zinc – particularly in lozenge or syrup form – “inhibits replication of the virus” that cause the common cold and shortens average duration of the common cold when taken within 24 hours of onset of symptoms at a dose of more than 75 milligrams a day.
A 2010 study led by University of Leiden Medical researchers in the Netherlands sought to understand how zinc inhibited that replication. The team reported that zinc inhibits a cousin of SARS-CoV-2: SARS-CoV, the original SARS of the 2003 outbreak.
Zinc is needed for immune cell development and communication and plays an important role in inflammatory response.
A deficiency in this nutrient significantly affects your immune system’s ability to function properly, resulting in an increased risk of infection and disease, including pneumonia.

Numerous studies reveal that zinc supplements may protect against respiratory tract infections like the common cold.
So, the question remains is hydroxychloroquine effective for COVID-19?
Until we have more data, from the additional trials listed above, the answer is still, we don’t know.
I will continue to follow the research and monitor what my colleagues are reporting from the front lines.
Until we have a proven drug or drugs, I recommend my patients do what they can to get healthier AND PREVENT getting infected.
You should continue to practice social distancing and if possible limit exposure to others when returning to regular daily activities.
For those who need to boost their immune system I’m recommending these preventative supplements to my patients.
All Immune Boosting Supplements Are On Sale! –> LEARN MORE | BUY NOW
My Gift To The Fibromyalgia Community
Beginning Tuesday April 7th 2020 I’ll be donating my time and holding a series of FREE Jump Start Your Health Training sessions. Over the next few weeks I’ll be sharing 20 years worth of expert fibromyalgia advice.
Each Tuesday at noon CDT, I’ll be on LIVE on FaceBook –> The Your Fibro Doctor Page
Each week I’ll focus on a new protocol to help you fix the underlying causes of your fibro symptoms. I’ll be sharing step-by-step protocols for how to dramatically depression. I’ll also answer your questions.
These Training Sessions Are Free! Anyone can attend. I’m donating my time and paying my staff to help me make these online training sessions available.
To get the most out these FREE training sessions we will sometimes include a FREE video or report. If you’d like to get these FREE resources then please let us know by sharing your email below.
*Your email will not be spammed or sold, ONLY used for OUR training and news emails.
Here Is The Replay Of The First Tuesday Jump Start Training:
ALSO – Each and every Wednesday I hold a Facebook LIVE Fibromyalgia Q&A. Tuesday training sessions will be just that, training sessions. Wednesdays will be reserved for general health information and Q&A
ARE YOU NEXT?





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!