Join Me For The 2 Week Detox Diet Challenge!
Scientists believe that the average person hosts about 500 toxic chemicals in his/her body, mostly within their fat tissues. These toxins may lead to serious health conditions such as infertility, liver damage, diabetes, brain damage, cancer, or death.
Ridding yourself of toxins through a healthy detox diet, combined with the right nutrients can help you:
- Dramatically increase your energy
- Reduce chronic achy pain
- Boost mental clarity
- Lose weight (if needed)
- Eliminate bloating, gas and other GI symptoms
- Remove excess water retention (swollen hands, ankles and feet)
- Have glowing, healthy skin, nails and hair
Step-by-step instructions, presentations, live Q&A sessions and more!
- Easy to follow diet, SAFE, gentle protocols (NO harsh chemicals or supplements, cleanses or purges!).
- By simply changing your diet and adding a couple of inexpensive over the counter supplements (optional), you can dramatically reduce your toxic load.
–> Learn more – Register for FREE HERE
to get information on accessing the FREE Zoom presentation, Q&A’s, handouts, recipes and more!
** If you can’t commit to doing the Detox Diet during the scheduled 2 weeks, simply grab the information and do it at your convenience. **
Register here and get your free registration gifts including, “What You Should Know About Organic Foods” Report
Detox To Get Healthy
We are constantly being exposed to potentially dangerous toxins through the food we eat, the air we breathe, and the water we drink. Thankfully, our liver works to neutralize harmful chemicals, viruses, and bacteria. It’s also first to process the nutrients delivered by the bloodstream.
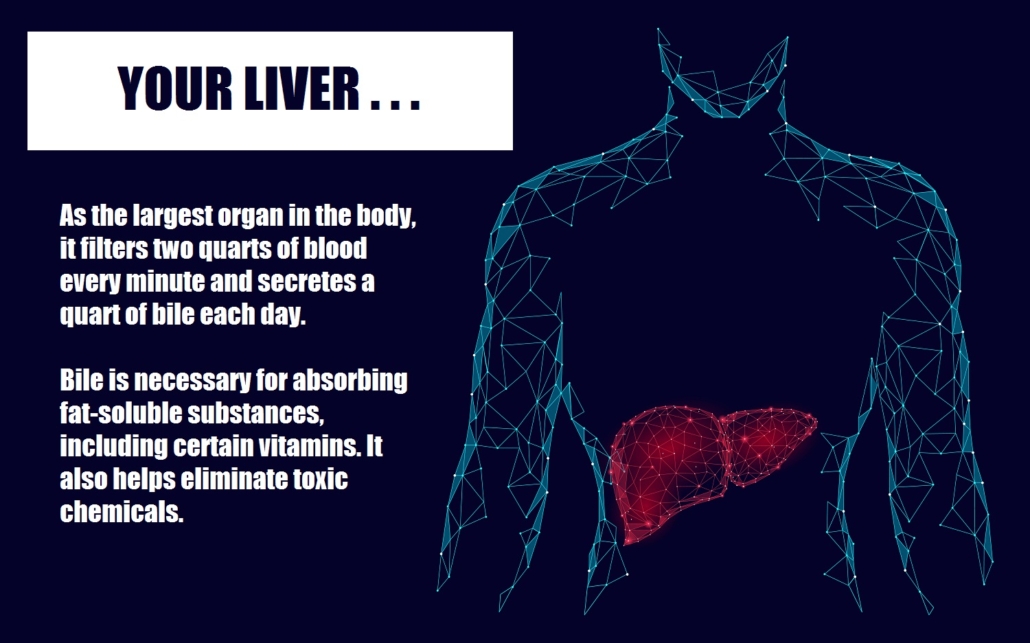
Bile is then mixed with dietary fiber and voided through daily bowel movements.
An optimally functioning detoxification system is necessary for providing good health and preventing disease. Many diseases, including cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other chronic age-related conditions, are linked to a weakened detoxification system.
A poor detox system also contributes to allergic disorders, asthma, hives, psoriasis, and eczema. It’s associated with chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, depression, and systemic candidiasis.
Two Phases of Detox
Unwanted chemicals, including prescription and nonprescription drugs, alcohol, pesticides, herbicides, and metabolic waste products are neutralized by the liver’s enzymes. There are two enzymatic pathways, phase I and phase II.
Phase I detoxification enzymes are collectively known as cytochrome P450. The cytochrome P450 system is made up of fifty to one hundred enzymes that attempt to neutralize toxic chemicals by transforming them into a less toxic form. Each enzyme is specially suited to certain types of toxins.
Chemicals that can’t be neutralized are changed into an intermediate form. As the phase I enzymes neutralize toxins, they spin off free radicals. If there aren’t enough antioxidants to counter these free radicals, the liver may be compromised.
Phase I detoxification is inhibited by antihistamines, NSAIDs, azole drugs (antifungals), tranquilizers such as Valium and Klonopin, and antidepressants such as Prozac and Celexa.
Is it any wonder that many chronically ill patients are told that their condition is “all in their head” when drugs make them sicker?

Phase I is responsible for neutralizing most over-the-counter and prescription drugs, caffeine, hormones, yellow dyes, insecticides, alcohol, and antihistamines. Do you get funny reactions when you drink alcoholic beverages or take antihistamine medication?
Phase II detoxification enzymes go to work on the toxins that the phase I enzymes turned into intermediate form. They do this by attaching minute chemicals to the structures. This process is called conjugation, and it neutralizes the toxins, making them more likely to be excreted through urination or defecation.
Unfortunately, many of these intermediate forms are more toxic and potentially more damaging than in their original state. So an inadequate phase II detoxification system can cause all sorts of chronic illnesses.
A person suffering from poorly functioning phase II and overactive phase I detoxification is known as a pathological detoxifier.
These individuals fill up doctors’ offices on a regular basis, because they suffer from a variety of ailments that seem to never go away. One illness is replaced by another as the patient tries one prescription after another. Neither the doctor nor the patient realizes that a compromised detoxification system is being further aggravated by toxic prescription medications.
Phase II, is responsible for neutralizing acetaminophen, nicotine, and insecticides, is composed of the following processes:
› Glutathione conjugation requires vitamin B6 and the tri-peptide (made from three amino acids) glutathione.
› Amino-acid conjugation requires the amino acid glycine. Low-protein diets and deficient digestive enzymes inhibit this process. Individuals with hypothyroidism, arthritis, hepatitis, and chemical sensitivities may suffer from poor amino-acid conjugation.
› Methylation requires S-adenosyl-methionine (SAMe). SAMe is synthesized from the amino acid methionine and dependent on folic acid, choline, and vitamin B12. Methylation detoxifies estrogen, testosterone, thyroid hormones, acetaminophen, and coumarin.
› Sulfation requires the amino acids cysteine and methionine and the mineral molybdenum. Sulfation is involved in processing steroids, thyroid hormones, food additives, certain drugs, and neurotransmitters.
Individuals who can’t take certain antidepressants or have reactions to certain sulfur containing foods may benefit from taking extra molybdenum, taurine, cysteine, and methionine.
› Acetylation requires acetyl-CoA and is inhibited by a deficiency in vitamin C, B2, or B5. This pathway is responsible for eliminating sulfa drugs, so individuals with sulfa allergies may benefit from extra vitamin C, B2, or B5.
› Glucuronidation requires glucoronic acid and detoxifies acetaminophen,
morphine, benzoates, aspirin, and vanilla. Aspirin inhibits this process. Signs of deficiency include yellowish pigment in the eyes or skin not caused by hepatitis.
› Sulfoxidation requires molybdenum and detoxifies sulfites and garlic. You may be deficient in this enzyme if you have allergic reactions to sulfite foods or garlic, asthmatic reactions after eating, or a strong urine odor after eating asparagus. Individuals with a sluggish sulfoxidation pathway may benefit from taking additional molybdenum.
Free Radicals and Antioxidants:
Free radicals are unstable atoms or molecules with an unpaired electron in the outer ring. They fill the void by taking an electron from
another molecule, which then becomes unstable, needing another electron of its own. This sets up a destructive cycle that can cause damage to our bodies inside and out.
Internal metabolic activities, including immune and detoxification processes, generate free-radical molecules, but sometimes they come from our environment.
External sources include radiation, alcohol, tobacco, smog, medications, and pesticides. Free radicals have been implicated in such conditions as rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, cancer, and heart disease.
Believe it or not, oxygen is responsible for the creation of most toxic free radicals. Just like it causes rust on a car, excessive oxygen can cause premature aging and dysfunction in the body. That’s why antioxidants, including vitamins A, E, and C, and beta carotene, are so important. Along with the amino acids cysteine, methionine,
glycine, and glutathione (tri-peptide), they help deter the effects of free-radical damage.
Have you ever cut open an apple and then left it out awhile? If so, you’ve witnessed free radical damage.

Fish oils, SAMe, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage all stimulate phase I and phase II reactions. Choline, betaine, methionine, vitamin B6, folic acid, and vitamin B12 (altogether known as lipotrophic factors) stimulate bile production and its flow to and from the liver. Lipotrophic factors also increase SAMe and glutathione, which in turn spare the liver free-radical damage.
Glutathione is a potent antioxidant created by the body and involved in several critical-for-life functions.
Stay tuned for more information about toxins and protocols to remove them.
Get Your Free Detox Report When You Register For The 2 Week Detox Diet Challenge
Step-by-step instructions, presentations, live Q&A sessions and more.
Easy to follow diet, SAFE, gentle protocols (NO harsh chemicals or supplements, cleanses or purges!).
By simply changing your diet and adding a couple of inexpensive over the counter supplements (optional), you can dramatically reduce your toxic load.
–> Learn more – Register for FREE HERE
to get information on accessing the FREE Zoom presentation, Q&A’s, handouts, recipes and more!






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!